圖論應用題 驗證二元樹節點 Validate Binary Tree Nodes_Leetcode #1361
閱讀時間約 5 分鐘
題目敘述
題目會給我們節點總數目n、左子樹的關係陣列、右子樹的關係陣列,要求我們驗證在給定的條件下,能不能構成一顆合法的二元樹。
測試範例
Example 1:
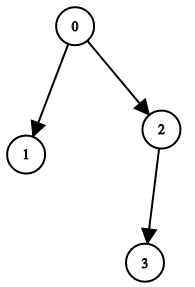
Input: n = 4, leftChild = [1,-1,3,-1], rightChild = [2,-1,-1,-1]
Output: true
Example 2:
Input: n = 4, leftChild = [1,-1,3,-1], rightChild = [2,3,-1,-1]
Output: false
Example 3:
Input: n = 2, leftChild = [1,0], rightChild = [-1,-1]
Output: false
約束條件
Constraints:
n == leftChild.length == rightChild.length1 <= n <= 104-1 <= leftChild[i], rightChild[i] <= n - 1
演算法
先找出根結點,根結點Root不會是別人的子樹,所以根結點Root一定不會出現在leftChild和RightChild這兩個關係陣列。
如果根結點Root找不到,代表樹根不存在,樹根不存在可以提早返回False,代表這不是一顆合法的二元樹。
如果根結點找的到,那接下來就用經典的DFS或者BFS,以根結點Root為起始點,拜訪整顆二元樹。
假如最後剛好拜訪n個節點,並且沒有重複,那麼就可以驗證這是一顆合法的二元樹。
如果有重複拜訪,代表途中存在環路,二元樹不允許環路Cycle出現,直接返回False,代表這不是一顆合法的二元樹。
程式碼
class Solution:
def validateBinaryTreeNodes(self, n: int, leftChild: List[int], rightChild: List[int]) -> bool:
# Definition of NULL (i.e., empty node), given by description
NULL = -1
# --------------------------------------------------------------
def find_root():
children = set(leftChild) | set(rightChild)
# search for root node, root node is not a child node always.
for i in range(n):
if i not in children:
return i
return NULL
# --------------------------------------------------------------
root = find_root()
if root == NULL:
# Reject, because root doesn't exist
return False
# launch BFS to given graph
queue = deque([root])
visited = set()
while queue:
cur = queue.popleft()
if cur in visited:
# Reject, because there is a cycle
# Cycle is not allowed in binary tree
return False
visited.add(cur)
if leftChild[cur] != NULL:
queue.append( leftChild[cur] )
if rightChild[cur] != NULL:
queue.append( rightChild[cur] )
# BFS in binary tree must visit n nodes exactly, without repetition.
return len(visited) == n
複雜度分析
時間複雜度: O( n)
定位根結點耗費O(n),拜訪整棵樹也耗費O(n)
空間複雜度: O(n)
演算法中,建立了一個children集合,所佔用記憶體空間為O(n)
BFS拜訪所用到的Queue或者DFS拜訪所用到的Stack,佔用空間最多也為O(n)
關鍵知識點
拜訪二元樹,就想到經典的DFS和者BFS模板。
另外,二元樹裡面,不允許環路Cycle出現。
Reference:
[1] Python O(n) by DFS / BFS / UnionFind [w/ Comment] - Validate Binary Tree Nodes - LeetCode
86會員
425內容數
由有業界實戰經驗的演算法工程師,
手把手教你建立解題的框架,
一步步寫出高效、清晰易懂的解題答案。
著重在讓讀者啟發思考、理解演算法,熟悉常見的演算法模板。
深入淺出地介紹題目背後所使用的演算法意義,融會貫通演算法與資料結構的應用。
在幾個經典的題目融入一道題目的多種解法,或者同一招解不同的題目,擴展廣度,並加深印象。
留言0
查看全部




















